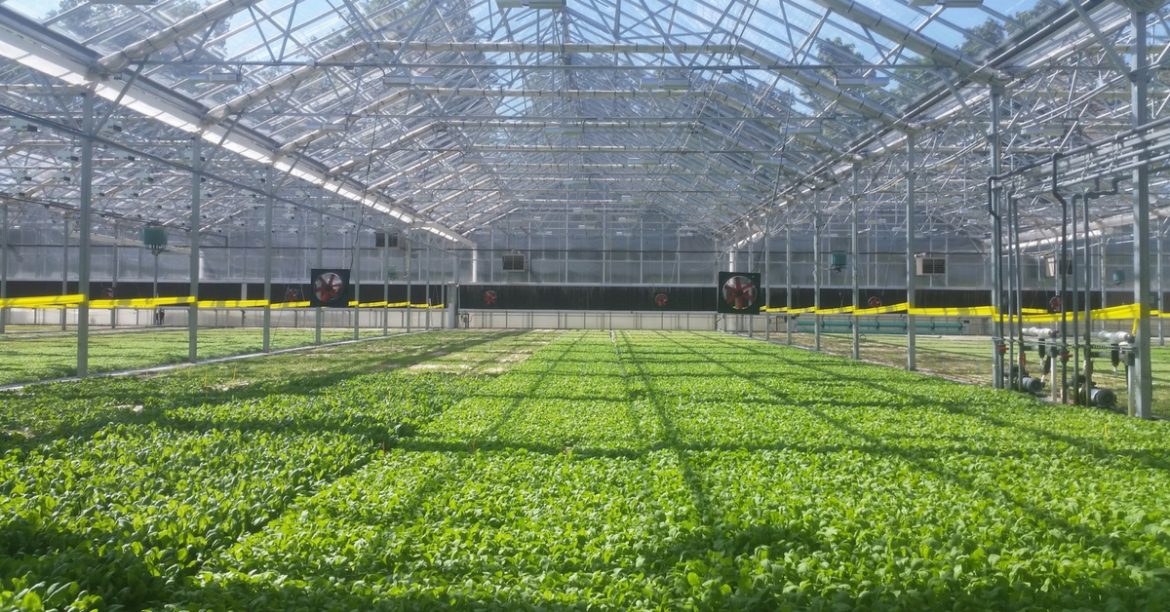
Day 4 on our Sustainable Farming Program was a trip all the way out the Pennsylvania to visit Bright Farms. Bright Farms builds and operates green house farms that grow produce by hydroponic farming.
Hydroponic farming…what’s that?
First, let’s start off with identifying a few different types of farming.
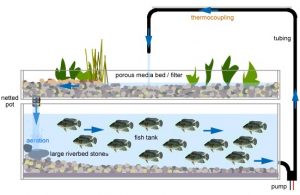
Aquaponics
Aquaponic Farming is a closed loop system. Aquaponics refers to farming, in water, where the plants rely on nutrients obtained from fish waste (aka fish poop.) The plants use the nutrients from the fish waste as fertilizer. Other than using the water with fish waste to grow, the plants also filter the water and release it back into the system. Check out this diagram below to get a better understanding.
Hydroponics
Hydroponic Farming is the farming method Bright Farms uses to grow plants and produce. Hydroponic Farming, instead of using soil, uses a mineral solution which is released into the water, where the roots of the plants are exposed, and is absorbed through the roots.
Pros of Hydroponic Farming:
- 80% less water is used (compared to growing these plants outside)
- Preserves space
- No runoff problems
- Preserves nutrients
Cons of Hydroponic Farming:
- In the winter, CO2 in the air is depleted (growing in a greenhouse)
- Have to reintroduce CO2 back into the air, often artificially, by using: natural gas or opening the windows on the greenhouse, which results in losing heat (problematic in winter)
Take a look below to see how Bright Farm’s grows with hydroponics.


Bright Farms grows a large array of greens and tomatoes through Hydroponic Farming. Head over here to find out where and what you can purchase from them!
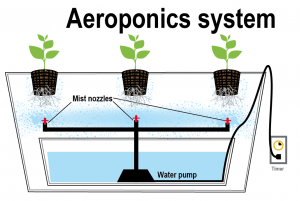
Aeroponics
Aeroponic Farming is almost identical to hydroponic farming, but instead of using floating planters, like hydroponics does, the plants are suspended in the air via a support system and exposed to mist to grow.
So, now that you know a little bit about these 3 types of farming, which ones your favorite? Let us know!
 Food
Food Farmers
Farmers Sustainable Living
Sustainable Living Living Planet
Living Planet News
News